Researchers in the Institute of Industrial Science at The University of Tokyo studied a new method for creating semisolid colloidal systems with less internal mechanical stress by delaying network formation. This work may help scientists better understand biological processes involving cytoplasm.
Within soft-matter physics, gels are a relatively familiar sight. Certain particle suspensions can be turned into a semisolid when particles join to form a stiff network. Think of Jell-O, in which a soupy mix of gelatin proteins sets into a delicious, free-standing dessert. Gels play important roles in biology, and may be involved in how cells move and respond to changing external conditions.
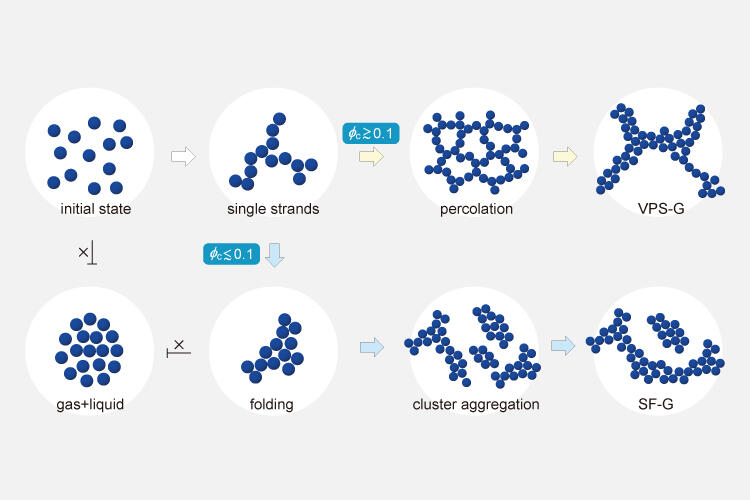
Scientists at The University of Tokyo studied the mechanism by which dispersed particles, called colloids, join together during gelation. Most gel networks are thought to form before dynamical motion stops, which leads to built-in mechanical stress. If the creation of the networks could be delayed, they could be made free from such stress and more stable .
"A net under mechanical tension is stretched and sometimes broken. Conventional colloidal gels suffer from such stress, and thus, are not so stable. Stress-free gels are free from this problem," first author Hideyo Tsurusawa explains.
The team found that network formation (percolation) occurs after the formation of a mechanically stable structure and the cessation of particle motion for a lower concentration of colloidal particles compared with the one at which traditional gels form. The researchers used confocal microscopy and computer simulations to better understand both conventional and stress-free gelation. Systems with fluorescently-labeled poly(methyl methacrylate) colloids could be monitored to see how long it took for networks to form and for particle motion to be arrested.
The choice between these two types of gelation is determined by the large and small relationship between the two characteristic times, i.e., "time until the mechanically stable structure is formed" and "time to percolation". Furthermore, when the interaction between the particles is short-range, the large and small relationship is determined solely by the volume fraction of the colloid.
"We found that colloidal gelation can universally be grouped into the two types. This universal classification of the gelation of particle systems is expected to make a significant contribution to the understanding of gelation in the field of soft matter and biology.," senior author Hajime Tanaka says. "Our findings could be applied to developing new industrial processes that create semisolid products, including foodstuffs, more efficiently."
###
The work is published in Science Advances as " A unique route of colloidal phase separation yields stress-free gels." (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abb8107)
Research Contact
Hajime Tanaka, Professor Emeritus
Institute of Industrial Science, the University of Tokyo
Tel: +81-3-5452-6125 Fax: +81-3-5452-6126
E-mail: tanaka (Please add "@iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp" to the end)
URL: http://tanakalab.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/